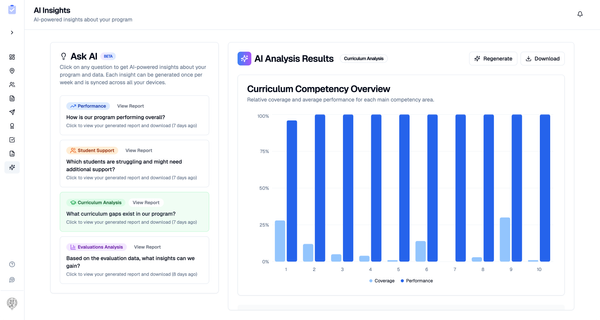
How often should you check vital signs?

The frequency of vital sign checks in different hospital units can vary based on several factors, including the patient's condition, level of acuity, and the specific protocols of the hospital. Here's a general overview of the frequency of vital sign checks in common hospital units:
Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
Vital signs are typically checked very frequently in the ICU, often every 15 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the patient's stability and criticality. This frequent monitoring allows for close observation and prompt intervention if any significant changes occur.
Medical-Surgical Units
In medical-surgical units, the frequency of vital sign checks can vary depending on the patient's condition. Typically, vital signs are checked every 4-8 hours, or more frequently if the patient is unstable or requires closer monitoring.
Telemetry (Tele) & Step-Down Units
On tele and step-down units, vital signs are typically checked every 4 hours but could require more frequent checks based on the patient's condition.
Emergency Department (ED)
In the ED, vital signs are often checked upon arrival and assessed periodically based on the patient's condition and the urgency of care required. The frequency can vary widely depending on the severity of the presenting symptoms or injuries.
Pediatric Units
In pediatric units, the frequency of vital sign checks depends on the child's age, condition, and the healthcare provider's judgment. Vital signs are typically checked every 4-8 hours, but more frequent monitoring may be necessary for critically ill or unstable pediatric patients.
Obstetrics Units
In obstetrics units, vital signs are typically monitored during labor and delivery, as well as postpartum. The frequency of vital sign checks may vary based on the stage of labor and the specific circumstances but can range from every 15 minutes to hourly during active labor.
It's important to note that these are general guidelines, and the frequency of vital sign checks can be adjusted based on individual patient needs, hospital policies, and the healthcare provider's judgment. In critical or rapidly changing situations, vital signs may be monitored more frequently for timely intervention.